3 minutes
Study of Capacitors
Understanding Capacitors: A Study
A capacitor is an electronic component that stores electrical energy in an electric field. Capacitors are widely used in electrical circuits for a variety of purposes, including filtering, coupling, and energy storage.
Diagram
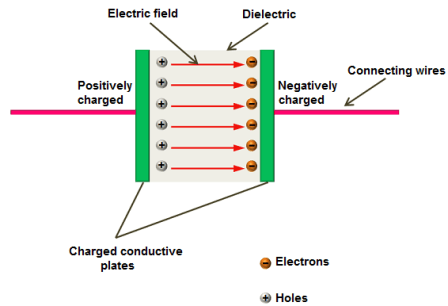
Basic Capacitor
Diagram: Diagram of a basic capacitor
Theory
Working of Capacitor
A capacitor is a two-terminal electronic component that stores electrical energy in an electric field. The theory of working of a capacitor is based on the principle of electrostatics, which states that opposite charges attract and like charges repel. When a voltage is applied across the terminals of a capacitor, it causes an electric field to develop between two conductive plates, separated by an insulating material known as a dielectric. The strength of the electric field is proportional to the voltage across the capacitor and the capacitance, which is a measure of the amount of electrical charge that can be stored per unit of voltage. When the voltage is removed, the electric field collapses and the energy stored in the electric field is released, making capacitors useful in a variety of applications such as power supplies, filters, and energy storage.
Types of Capacitors
There are many different types of capacitors available, each with its own unique characteristics. Some common types include:
- Aluminum electrolytic capacitors: These capacitors have a high capacitance and are commonly used in power supplies and audio equipment.
- Ceramic capacitors: These capacitors have a low cost and are commonly used in circuits where a small value of capacitance is needed.
- Film capacitors: These capacitors have a high dielectric strength and are commonly used in high voltage and high frequency applications.
- Supercapacitors: These capacitors have a very high capacitance and can store a large amount of energy. They are commonly used in applications such as energy storage and backup power.
Uses of Capacitors
Capacitors are used in a wide variety of applications, including:
- Power supplies: Capacitors are used to smooth out the output of power supplies and to filter out unwanted noise.
- Audio equipment: Capacitors are used in audio equipment to block DC signals and to allow AC signals to pass through.
- Motor controls: Capacitors are used in motor controls to provide a “boost” of energy to start the motor.
- Signal processing: Capacitors are used in signal processing circuits to filter out unwanted signals and to adjust the phase of signals.
Charging and Discharging a Capacitor
When a capacitor is connected to a voltage source, an electric field is established between the plates of the capacitor, which causes charges to accumulate on the plates. The amount of charge that accumulates on the plates is directly proportional to the voltage applied to the capacitor. This process is known as charging the capacitor.
The rate at which a capacitor charges depends on the capacitance and the resistance in the circuit. The capacitance of the capacitor determines how much charge it can store for a given voltage, and the resistance in the circuit determines how quickly the charges can flow to the capacitor.
When a capacitor is disconnected from a voltage source, the charges on the plates will begin to flow back to the circuit, and the voltage across the capacitor will decrease. This process is known as discharging the capacitor. The rate of discharging also depends on the capacitance and the resistance in the circuit. A capacitor can be charged and discharged many times and it will not lose its capacitance.
In this video, we can see how a capacitor behaves when charging and discharging.
Conclusion
Capacitors are essential components in many electrical circuits, and they play an important role in many applications. Understanding how capacitors work and how they are used can help you to design and build more efficient and reliable circuits.
622 Words
2023-01-28 18:57