2 minutes
Study of Dmm
Summary
This topic aims to provide an in-depth understanding of digital multimeters, including its construction, components, and various applications.
Diagram
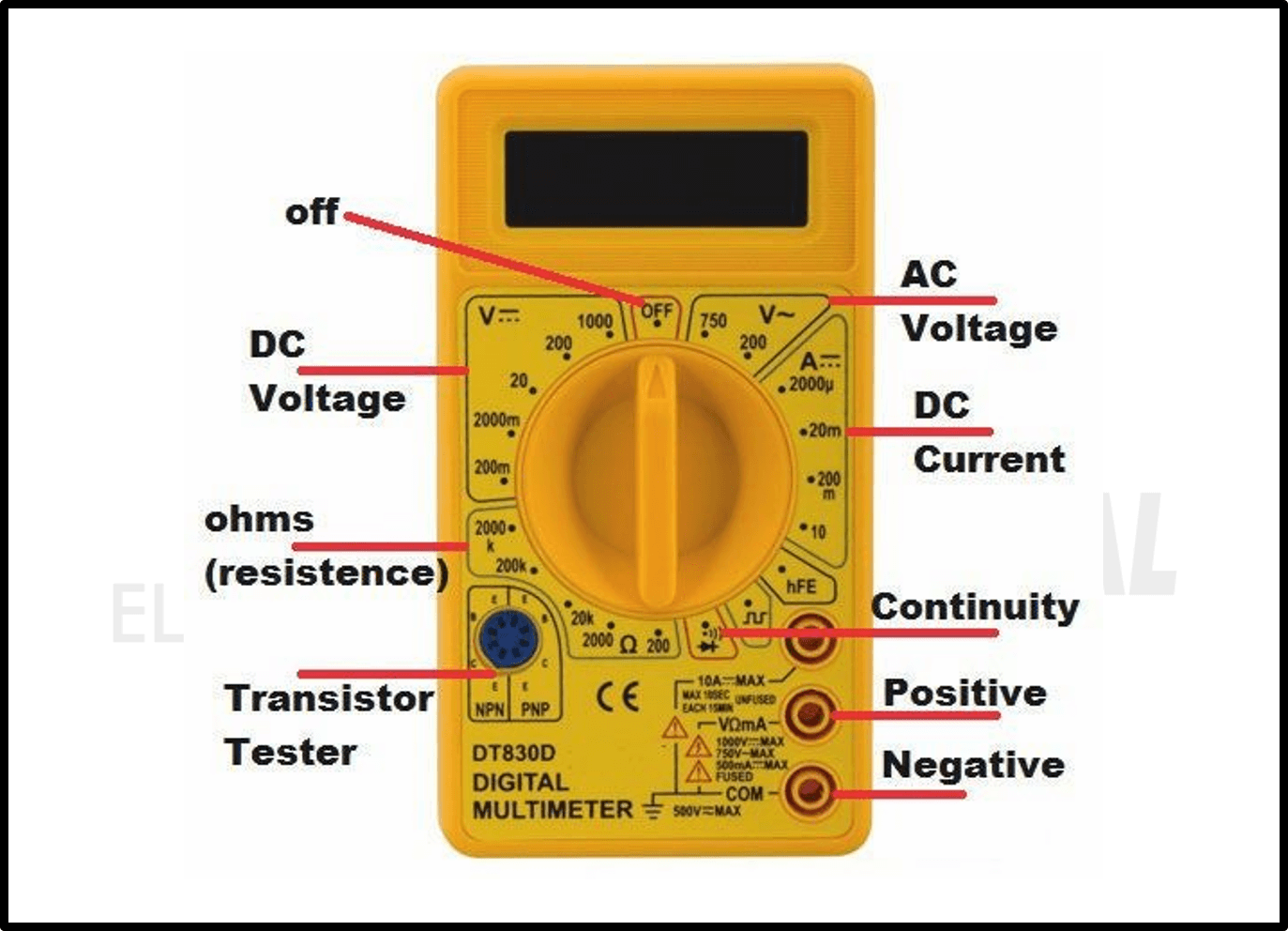
Basic DMM
Parts and Specifications
| Part | Specification |
|---|---|
| Display | LCD or LED |
| Range Selection | Manual or Auto Ranging |
| Input Impedance | >10 MΩ |
| Maximum Voltage | 600V AC/DC |
| Maximum Current | 10A AC/DC |
| Resistance | 200Ω to 200MΩ |
| Continuity Test | Built-in Buzzer |
| Diode Test | Built-in |
Tools and Instruments
- Digital multimeter
- Lead set
- 9V battery
- Circuit under test
Procedure
The procedure for using a digital multimeter is quite straightforward. First, select the appropriate range for the measurement to be taken. Then, connect the leads to the multimeter and to the circuit under test. Finally, observe the reading on the display. It is important to note that the polarity of the leads should be observed, as some measurements require the leads to be connected in a specific way.
Theory

Working of DMM
A digital multimeter is an electronic measuring instrument that can measure several electrical parameters such as voltage, current, resistance, and continuity. Digital multimeters use an ADC (Analog-to-Digital Converter) to convert the analog signals into digital signals for display on a screen.
The input impedance of a digital multimeter is high, typically above 10 MΩ, which means that it has very little effect on the circuit being measured. This is important because it allows accurate measurements to be taken without disturbing the circuit under test.
Types of Digital Multimeters
There are two main types of digital multimeters: manual ranging and auto ranging. Manual ranging multimeters require the user to select the appropriate range for the measurement, while auto-ranging multimeters automatically select the correct range.
Another type of digital multimeter is handheld multimeters, which are compact and portable, and can be easily carried to the work site. Benchtop multimeters, on the other hand, are larger in size and are designed to be used in a laboratory or workshop setting.
Applications
Digital multimeters are widely used in a variety of industries, including electronics, electrical, and automotive. They can be used for troubleshooting and repairing electronic circuits, as well as for testing and measuring various electrical parameters in a circuit. Digital multimeters are also commonly used in educational settings for teaching electronics and electrical principles.
Conclusion
In conclusion, digital multimeters are an essential tool for anyone involved in the field of electronics and electrical work. They are versatile, accurate, and provide quick and reliable measurements, making them an indispensable tool for professionals and hobbyists alike.
406 Words
2023-01-28 18:56