4 minutes
Study of Inductors
An inductor is a passive electrical component that stores energy in a magnetic field when electric current flows through it. Inductors play a crucial role in many electrical circuits, from filtering to energy storage to regulation. In this study, we will delve into the construction, theory, and uses of inductors.
Construction of a Basic Air-Core Inductor
The basic air-core inductor can be constructed by wrapping a wire around a non-conductive core, such as air, plastic, or fiberglass. The number of turns, or coils, of wire used, along with the diameter and material of the wire, will determine the inductance of the inductor. To calculate the inductance, the formula L = N^2 * Μ_o * A / l can be used, where N is the number of turns, Μ_o is the permeability of free space, A is the cross-sectional area of the coil, and l is the length of the coil.
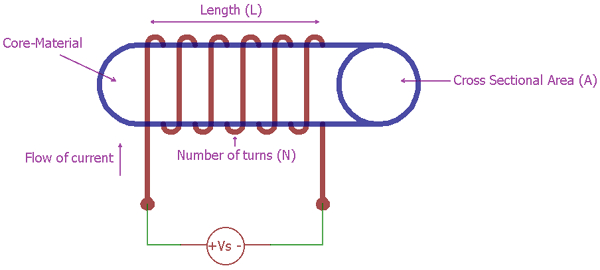
Basic Inductor
Diagram: A simple representation of an air-core inductor
Parts and Specifications
The following table lists the parts and specifications needed to construct a basic air-core inductor:
| Parts | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Wire | Enameled copper wire with a diameter of 0.5 mm |
| Core | Non-conductive material, such as air or plastic |
| Insulation tape | Electrical insulating tape to secure the ends of the wire |
Instruments, Equipments, and Tools
To construct an air-core inductor, you will need the following instruments, equipments, and tools:
- A wire stripper
- A spool of enameled copper wire
- A non-conductive core, such as air or plastic
- Electrical insulating tape
- A ruler or measuring tape
- A calculator
Procedure
The procedure for constructing a basic air-core inductor involves wrapping a wire around a non-conductive core and securing the ends of the wire. The steps for this procedure are explained in detail below:
- Determine the desired inductance and calculate the number of turns required.
- Cut a length of enameled copper wire to the desired length, plus an extra 10 cm for securing the ends.
- Strip the insulation from the ends of the wire.
- Wrap the wire around the non-conductive core to the desired number of turns.
- Secure the ends of the wire with electrical insulating tape.
- Test the inductance using a multimeter.
Theory
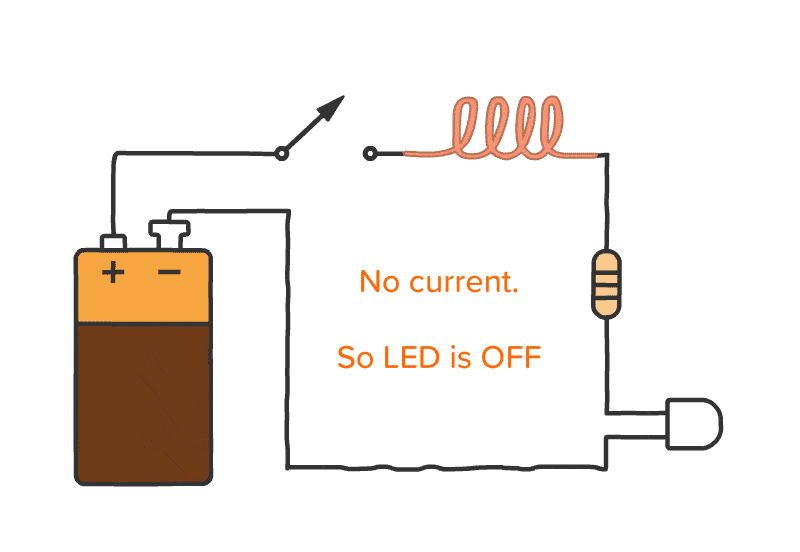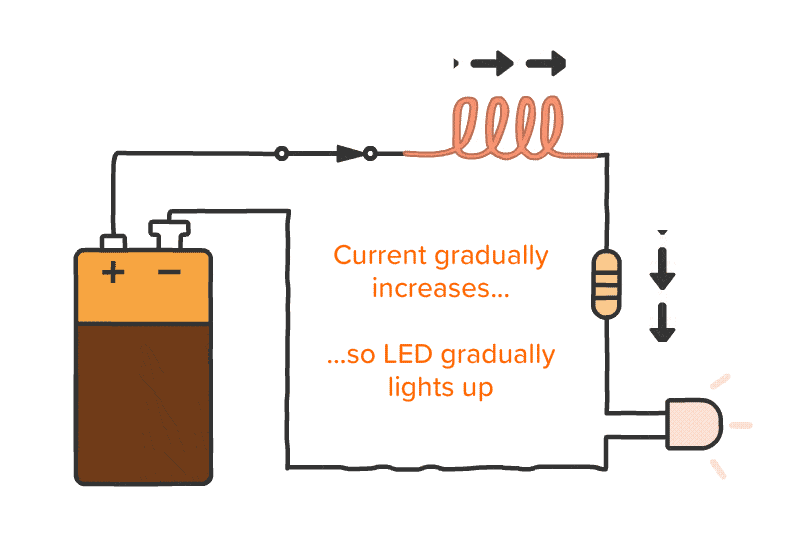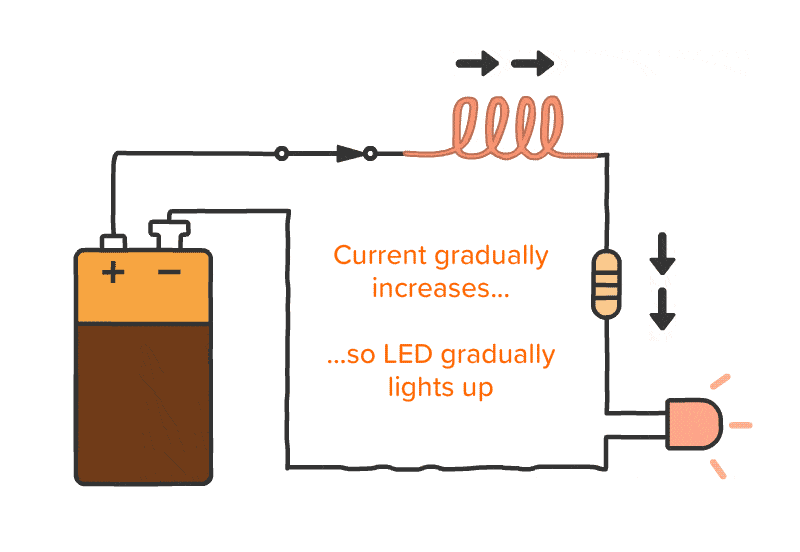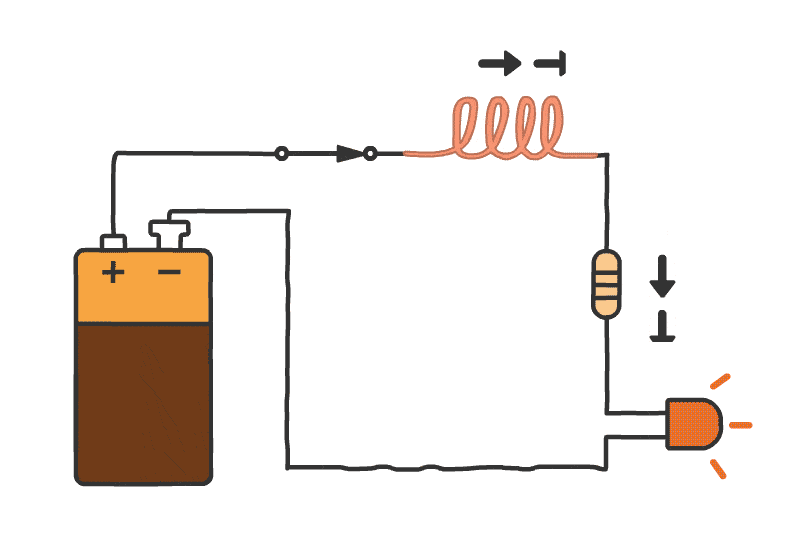
Working of Inductor
An inductor is a passive electrical component that stores energy in a magnetic field when electric current flows through it. The basic principle behind an inductor is Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction, which states that a changing magnetic field induces an electromotive force (EMF) in a conductor. The amount of energy stored in an inductor is proportional to the number of turns in the wire and the current flowing through it.
Types of Cores
There are several different types of cores that can be used in inductors, including air cores, iron cores, ferrite cores, and more. Each type of core has its own unique properties and advantages, making it ideal for specific applications.
Air cores are the simplest and most basic type of inductor core, and are ideal for applications that require a large inductance. They are also the most economical and easiest to manufacture.
Iron cores are used for high-frequency applications and provide a higher magnetic permeability than air cores. They also allow for a more compact design, as the magnetic field is concentrated in the core.
Ferrite cores are made of a magnetic ceramic material and are often used in high-frequency applications where a high impedance is required. They are also immune to temperature changes, making them ideal for use in temperature-sensitive applications.
Uses of Inductor
Inductors are widely used in electrical circuits for various purposes, including power supplies, filters, transformers, and resonant circuits.
One of the most common uses of inductors is in filters. Inductors are used in filter circuits to block or pass certain frequencies. A high-pass filter passes high-frequency signals and blocks low-frequency signals, while a low-pass filter passes low-frequency signals and blocks high-frequency signals.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Inductors are important components in electrical circuits, and understanding their construction, parts, instruments, procedure, theory, types of cores, and uses is crucial. With this knowledge, one can effectively design and implement inductors in various electrical circuits.
681 Words
2023-01-28 18:57