2 minutes
Study of Relay
Summary
This topic aims to provide an in-depth understanding of relays, including their construction, working principle, and various applications.
Construction of a Basic Relay
A basic relay consists of an electromagnet, a set of contacts, and a spring. When the electromagnet is energized, it attracts the armature, which then moves and closes the contacts.
Diagram:
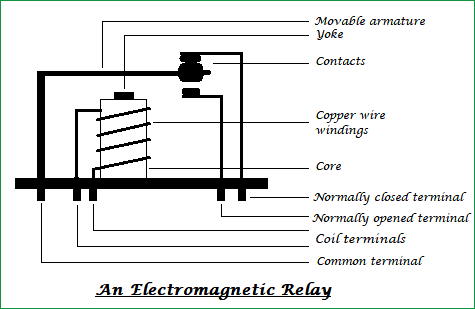
Basic Relay
Parts and Specifications
| Parts | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Electromagnet | Consists of a coil of wire, core, and a switch |
| Contacts | Typically made of metal and used to complete or break an electrical circuit |
| Armature | A movable piece of metal that is attracted by the electromagnet and responsible for closing the contacts |
| Spring | Used to return the armature to its original position when the electromagnet is de-energized |
Instruments and Tools Needed
- Multimeter
- Oscilloscope
- Soldering iron
- Wire stripper
- Pliers
Procedure
- Start by gathering all the necessary parts and tools.
- Assemble the electromagnet by winding the coil of wire around the core and soldering the leads to the switch.
- Mount the armature, contacts, and spring in their respective positions.
- Test the relay using a multimeter to verify that the contacts are opening and closing correctly when the electromagnet is energized and de-energized.
- Measure the voltage and current required to operate the relay using an oscilloscope.
- Finally, connect the relay to a circuit and test it under normal operating conditions.
Theory

Working of Relay
Relays are electrical switches that use an electromagnet to operate. When a voltage is applied to the coil of the electromagnet, it creates a magnetic field that attracts the armature, causing it to close the contacts. This closing of contacts completes the electrical circuit and allows current to flow. When the voltage is removed from the coil, the magnetic field collapses, and the spring returns the armature to its original position, opening the contacts and breaking the circuit.
Relays are useful in controlling high-power circuits with low-power signals, as well as in protecting sensitive electronic circuits from damage due to overloading.
Applications
Relays find applications in a wide range of fields, including automotive electronics, communication systems, industrial control systems, and home appliances. Some common applications of relays include controlling the operation of motors, switching on and off lights, and providing over-current protection to sensitive electronic circuits.
Conclusion
In conclusion, relays are an essential component in electrical and electronic circuits. They provide a simple and effective way to control and protect high-power circuits with low-power signals. Understanding the construction, working principle, and applications of relays is essential for anyone working in the field of electrical and electronics engineering.
421 Words
2023-01-28 18:57