3 minutes
Study of Transformer
Summary
A transformer is a passive electrical component that transfers electrical energy from one circuit to another through electromagnetic induction. In this study, we will learn about the construction and working of a basic transformer, different types of transformers, and their applications. We will also learn about the parts required to make a basic transformer and the instruments and equipment needed to perform this activity.
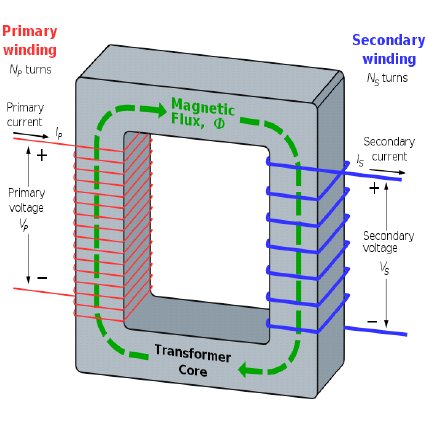
Basic Transformer
Parts and Specifications
A basic transformer consists of the following parts:
| Parts | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Copper Wire | Number of turns and gauge depends on the desired voltage and current rating |
| Iron Core | Magnetic permeability and cross-sectional area depends on the desired inductance |
| Insulating Material | High voltage insulation to prevent current from leaking from one coil to another |
Instruments and Equipment
The following instruments and equipment are required to perform this activity:
- Soldering iron
- Wire cutter
- Insulating tape
- Multimeter
- Power supply
Procedure
The procedure to make a simple transformer is as follows:
- Cut two pieces of copper wire to the desired length, with the number of turns and gauge depending on the desired voltage and current rating.
- Wrap the two pieces of wire around an iron core, with the magnetic permeability and cross-sectional area depending on the desired inductance.
- Insulate the two coils from each other using insulating material to prevent current from leaking from one coil to another.
- Solder the two ends of each coil to its own terminal.
- Test the transformer using a multimeter to measure the voltage and current ratings.
Theory
The basic theory behind a transformer is electromagnetic induction. When an alternating current flows through one coil, it generates a magnetic field that induces a voltage in the other coil. The voltage is proportional to the number of turns in each coil, the frequency of the alternating current, and the magnetic permeability of the core.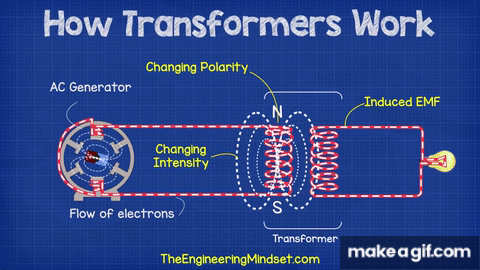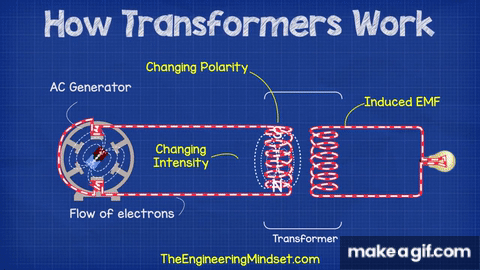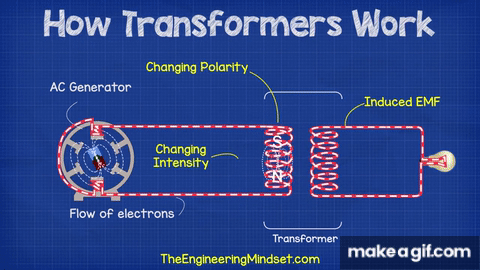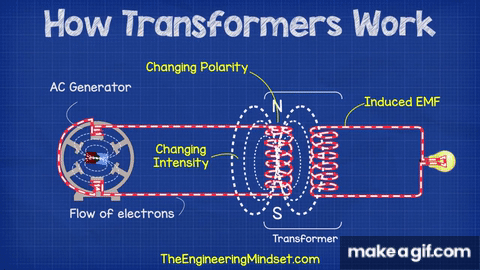
Working of Transformer
Types of Transformers
There are several types of transformers, including:
- Step-Up Transformer: Increases the voltage of the alternating current
- Step-Down Transformer: Decreases the voltage of the alternating current
- Isolation Transformer: Electrically isolates the two coils from each other, while still allowing energy transfer
- Auto Transformer: A type of transformer that uses a single winding instead of two separate windings
Uses of Transformers
Transformers are widely used in electrical power distribution systems to step up or step down the voltage of the alternating current, according to the requirements of the load. They are also used in electronic devices such as televisions, radios, and computers, to provide isolation and regulation of the power supply.
Conclusion
In conclusion, transformers play a crucial role in electrical power distribution and regulation. Understanding the construction, theory, and types of transformers is essential for anyone involved in electrical engineering and design. By performing the procedure described in this study, one can gain practical experience in building a basic transformer and gain a deeper understanding of this fascinating component.
477 Words
2023-01-28 18:57