3 minutes
Controllers and Operations - 1
Introduction to Microprocessors and Microcontrollers
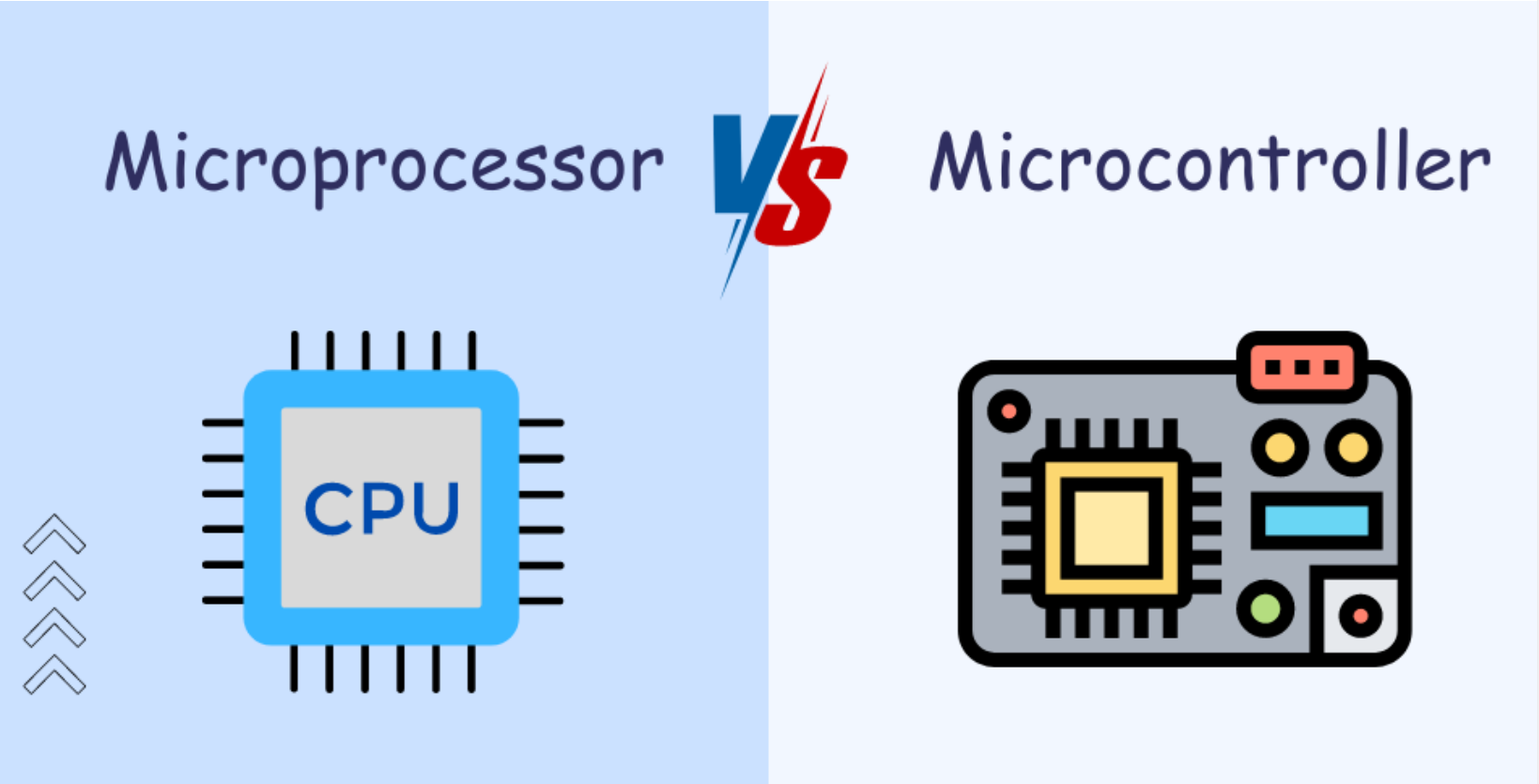
| Feature | Microprocessor | Microcontroller |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | General-purpose processor | Dedicated to specific tasks |
| Memory | External memory required | Includes internal RAM, ROM, and I/O ports |
| Application | Computers, laptops, high-performance devices | Embedded systems (IoT, appliances, etc.) |
| Cost | More expensive | Cost-effective for specific tasks |
| Examples | Intel 8086, Pentium, Core i5, i7, AMD Ryzen | 8051, AVR, PIC, ARM, ESP8266, ESP32, etc. |
- Q: Where are these examples present in day-to-day usage?
Applications of Microcontrollers
Common Applications
- Consumer Electronics: TVs, washing machines, microwave ovens
- Automotive: Engine control units, airbags, ABS
- Industrial Automation: Process controllers, robotics
- IoT Devices: Smart home systems, wearables
- Medical Devices: ECG machines, glucose monitors
Features of 8051 Microcontroller
- 8-bit microcontroller
- 4 KB ROM (programmable memory)
- 128 bytes RAM
- 32 I/O pins (organized into 4 ports)
- Two 16-bit timers/counters
- Full-duplex UART for serial communication Q: What is Full-duplex?
- Interrupt system with 5 sources
Architecture of 8051
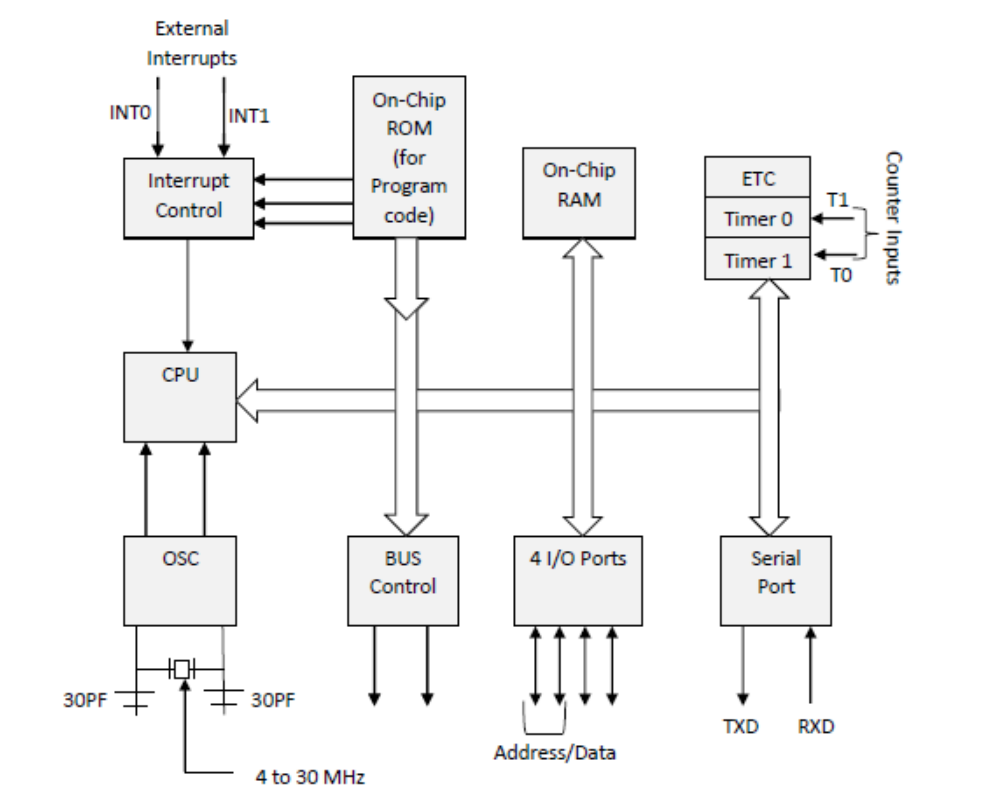
Key Components
- ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit): Performs arithmetic and logical operations.
- Registers: Accumulator (A), B register, general-purpose registers.
- Memory:
- Program memory (ROM)
- Data memory (RAM)
- I/O Ports: 4 bidirectional 8-bit ports.
- Timers/Counters: Two 16-bit timers.
- Serial Communication: UART.
- Interrupts: 5 interrupt sources, including external and timer interrupts.
Pin Diagram of 8051
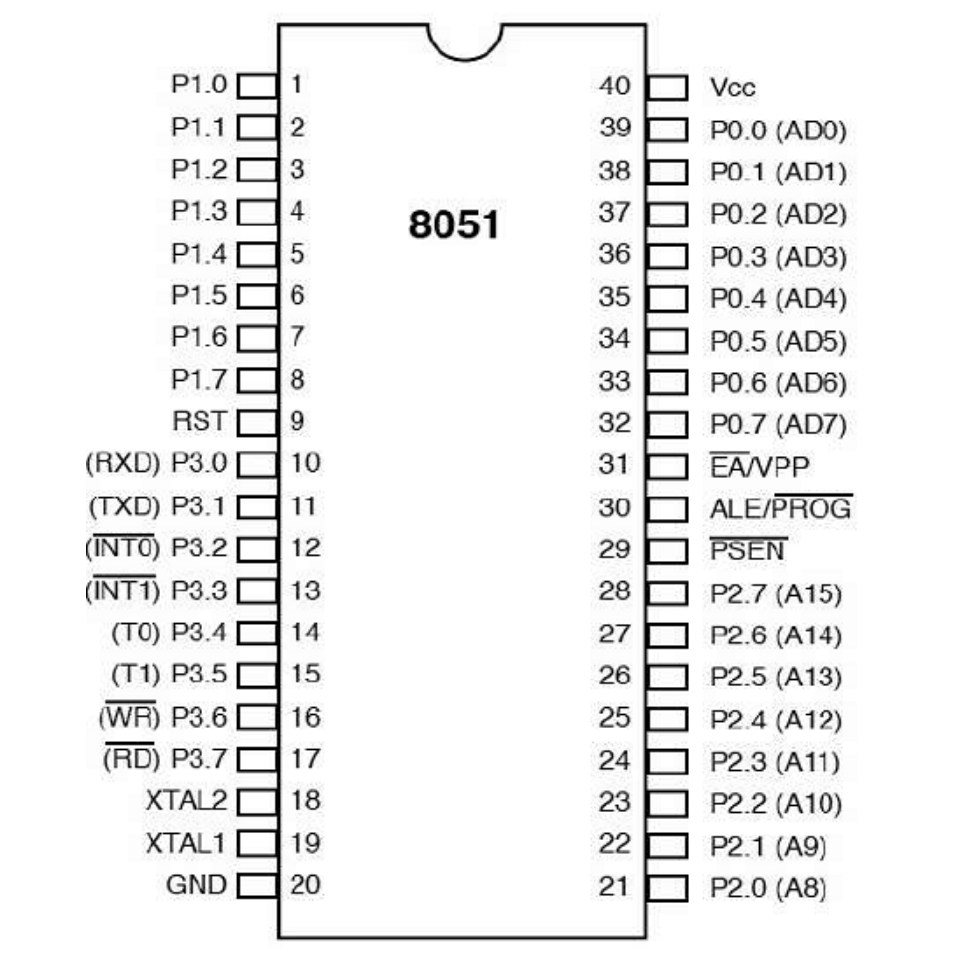
- Port P0 (Pins 32-39): Multiplexed as data and address bus.
- Port P1 (Pins 1-8): General-purpose I/O.
- Port P2 (Pins 21-28): High-order address bus in external memory interfacing.
- Port P3 (Pins 10-17): Dual-purpose (I/O + special functions like serial input/output).
- Other Pins:
- Vcc (Pin 40): +5V supply
- GND (Pin 20): Ground
- RST (Pin 9): Reset input
- EA (Pin 31): External Access enable
- ALE (Pin 30): Address Latch Enable
- PSEN (Pin 29): Program Store Enable
Memory Organization of 8051
Internal Memory
- RAM:
- 128 bytes divided into:
- 32 bytes: General-purpose registers (R0 to R7 for 4 banks).
- 16 bytes: Bit-addressable memory.
- 80 bytes: General-purpose memory.
- SFRs: Control I/O, timers, and serial communication.
- 128 bytes divided into:
- ROM:
- 4 KB for program storage.
- Address range: 0000H - 0FFFH.
External Memory
- Supports up to 64 KB of program memory and 64 KB of data memory.
- Uses Port 0 and Port 2 for data and address buses.
Interrupt Structure of 8051
Features of 8051 Interrupt System
- 5 interrupt sources:
- External Interrupt 0 (INT0)
- Timer 0 Overflow
- External Interrupt 1 (INT1)
- Timer 1 Overflow
- Serial Communication Interrupt
- Interrupt Priority Levels:
- Low priority
- High priority (overrides low-priority interrupts)
- IE (Interrupt Enable) Register:
- Enables or disables specific interrupts.
- IP (Interrupt Priority) Register:
- Sets priority levels for interrupts.
Interrupt Execution
- When an interrupt occurs, the microcontroller:
- Suspends the current task.
- Jumps to the corresponding Interrupt Service Routine (ISR).
- Resumes the main program after ISR execution.
Summary
- Microprocessor vs Microcontroller: Microcontrollers are specialized for embedded systems.
- 8051 Features: 8-bit architecture, 4 KB ROM, 128 bytes RAM, and 32 I/O pins.
- Applications: Widely used in IoT, automation, and consumer electronics.
- 8051 Architecture: Integrated ALU, memory, timers, and serial ports.
- Pin Diagram and Memory: Essential for hardware interfacing and program execution.
Questions and Discussion
- 2 doubts from each (minimum)
- In 1 line, tell what did you understood from this presentation.
References:
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/microprocessor/microcontrollers_8051_architecture.htm
502 Words
2025-01-14 00:04